Get Started With an IIoT Connectivity Plan
If you are looking to connect your operations to the Industrial Internet of Things, there a few things to consider before embarking on the journey. We’ve mentioned before that proper connectivity is critical for interoperability and without interoperability between devices, the IIoT is not possible. To lower the adoption curve of the Industrial IoT, there are some key connectivity device characteristics that you should look for when researching solutions. One other major point was around proving the value of your investment through calculating the payback.
All of these considerations tie very closely into the idea of developing a connectivity plan. With a connectivity plan, you’ll have a solid idea of what your organization is looking to achieve with the IIoT, what your current connectivity situation looks like, which devices you’ll need to help you meet your goals, and what the payback period for your investment will be. Below, we’ve outlined some helpful steps to get you ready and have included a download to our IIoT Connectivity Workbook to assist you in developing your connectivity plan.
All of these considerations tie very closely into the idea of developing a connectivity plan. With a connectivity plan, you’ll have a solid idea of what your organization is looking to achieve with the IIoT, what your current connectivity situation looks like, which devices you’ll need to help you meet your goals, and what the payback period for your investment will be. Below, we’ve outlined some helpful steps to get you ready and have included a download to our IIoT Connectivity Workbook to assist you in developing your connectivity plan.
Steps 1 & 2: Develop and Prioritize Your IIoT Goals
First and foremost, in order to develop your IIoT connectivity plan, you’ll want to have some goals established for your operations. You may have an idea of some key IIoT benefits that you’ll want to bring to your business, or you may just know that you want to get connected for future compatibility. Nonetheless, goal planning is a best practice for any project, large or small.
Within the goal planning process, you can follow these two easy steps to help pave the way.
Within the goal planning process, you can follow these two easy steps to help pave the way.
Step 1: Assess Your Operational Pain Points
Take a step back and look at your operations as they are running and identify any pain points (problems or areas for improvement) that you are currently experiencing. This could be anything from an unsatisfactory downtime rate, poor systems management, or control limitations. Regardless of the severity, you’ll want to document these pain points and list them together for reference.
Step 2: Develop and Prioritize Operational Goals
Now that you have your pain points listed, you’ll want to begin thinking about some operational goals or outcomes that you would like your business to achieve in order to address these pain points. Let’s say your pain point is around high equipment failure rates that result in increased downtime. An operational IIoT goal could be the following: “Implement predictive maintenance capabilities to help identify potential equipment failures before they occur.” Make sure to develop goals for every pain point that you have documented. Once this is done, set a priority level for each goal. This will help you determine which project is the most critical and will help you determine where to start first.
Step 3: Understand Your Current Interoperability Situation
Once you have your goals developed and prioritized, you’ll want to complete an audit of your existing equipment in your operation. List out all of the machinery involved in your operation as they relate to your goals. This audit should include information like types of equipment, manufacturers, protocols, physical interfaces,quantities and locations.
Make sure to also note any specific limitations or additional details that may be available. This will be important in helping you identify any protocol/interface gaps that you’ll need to fill and will help you determine the devices that you’ll need to achieve connectivity.
Make sure to also note any specific limitations or additional details that may be available. This will be important in helping you identify any protocol/interface gaps that you’ll need to fill and will help you determine the devices that you’ll need to achieve connectivity.
Step 4: Choose The Right Devices to Help You Get Connected
After completing your equipment audit and identifying the various protocols and physical interfaces within your operation, you’ll want to begin identifying solutions to help achieve interoperability. Within the connectivity space for the Industrial Internet of Things, there are three main types of solutions in the connectivity layer that can help you achieve interoperability. These areas are Edge Connectivity, Industrial Computing, and Network Infrastructure.
By learning more about each area, you’ll be able to better assess the types of devices that you’ll need to develop your IIoT connectivity solution. You’ll then want to begin map out specific solutions to your equipment audit so you can begin to close the connectivity gaps.
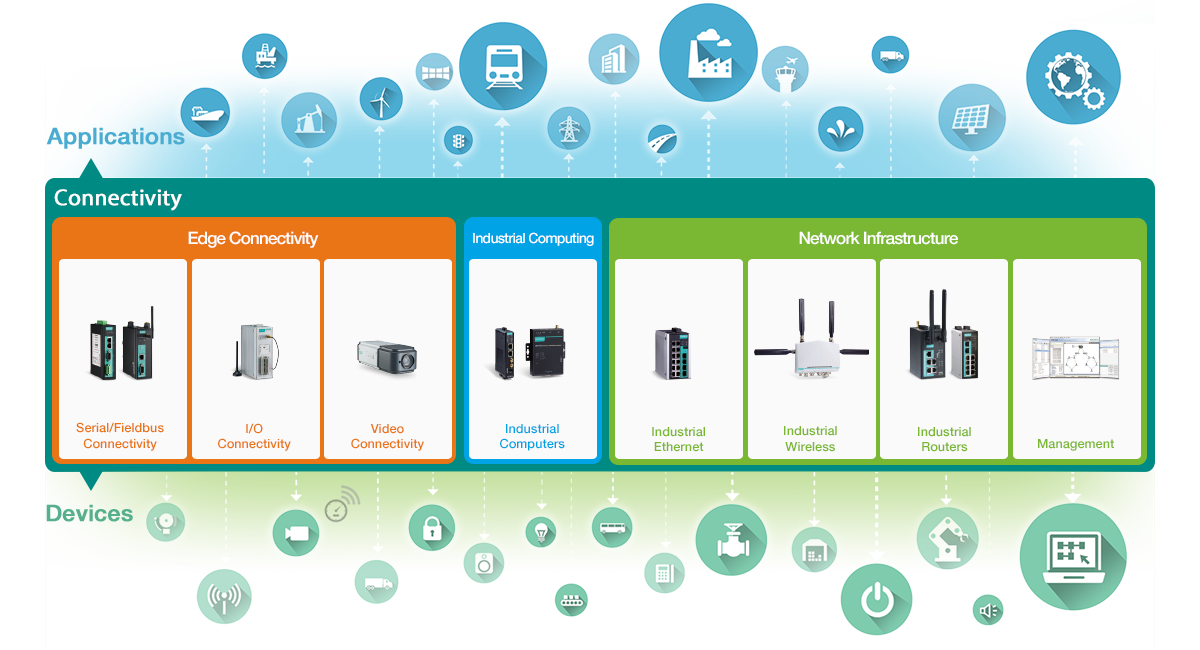
By learning more about each area, you’ll be able to better assess the types of devices that you’ll need to develop your IIoT connectivity solution. You’ll then want to begin map out specific solutions to your equipment audit so you can begin to close the connectivity gaps.

Edge Connectivity
Connecting factories and field networks to the industrial internet can be more complex than it seems. Industrial automation utilizes a medley of protocols that make open, scalable communication across factory sites very complicated and potentially cost prohibitive. The Industrial IoT is all about knocking down these communication barriers between sensors, machines and networks - delivering a global common language. Ethernet and wireless gateways are some examples that allow for IoT connectivity by simply integrating connectivity devices into existing infrastructure.Industrial Computing
Computing is no longer constricted to data centers and office desktops. Industrial Computing (or edge computing) is a central tenant and leading facilitator for the Industrial IoT. Bringing computation to the network’s edge, at the plant floor or field, allows industrial automation to become more intelligent and efficient. Edge computing allows operations to become predictive, rather than reactive in managing key assets and capital equipment. Whether it is discrete or process automation, carefully utilizing industrial edge devices with data logging capability or real time control, allows you to gain actionable intelligence from the flood of data originating from your various sensors, motors and actuators.Network Infrastructure
Network Infrastructure represents the nervous system of communication and control for an Industrial IoT solution. All network packets need to pass continuously between sensors, motors, actuators and the SCADA without risk of failure. To provide signal assurance, your network infrastructure needs to meet your industry’s industrial certification criteria, while accounting for physical redundancy and bandwidth requirements.Step 5: Justify Your Investment
After you’ve developed and prioritized your goals, completed an equipment audit, and have identified solutions to assess your connectivity needs, you’ll want to then be able to justify your investment. One way to do this that is pretty straightforward is being able to calculate the payback on your connectivity project. By taking multiple aspects into consideration such as your production rate, revenue potential, production costs, quality costs, service costs, and the cost of your investment, you’ll be able to calculate what the payback period on your investment will be.
We put together a payback calculator that is part of our IIoT Connectivity Workbook that can help you calculate the payback period for your own investment and help justify your adoption of the Industrial IoT.
Tools to get Started

To help you follow the steps listed above, download our Industrial IoT Connectivity Workbook to help.
This workbook includes some excellent templates and tools to help:
This workbook includes some excellent templates and tools to help:
- Goal Planning Worksheet
- Equipment Audit Worksheet
- Payback Calculator
If you need help with choosing the right devices for connectivity or just want more information, let us know. We'll have one of our representatives reach out to you.
Want more info like this?
Subscribe to learn more about the IIoT and Industrial Networking.